User experience and user interface - two different terms that often stand in opposition to each other, but do not work against each other at all! Rather, the two areas complete each other during the design process and work closely together. In this blog post, you can find out how user experience and user interface interact, what the two terms actually mean and what the tasks of UX and UI designers are.
What does UX Design mean?
UX Design is the short form for User Experience Design and, as the name already suggests, deals with the user experience. In general, UX design includes techniques and methods that are used to design and improve a product. UX design pursues the goal of user-friendly and flawless handling of the product and defines the structure of content and navigation in particular.
User experience design is also about the creative aspects of experiences. In addition to usability, the feeling and experience before, during and after use also play an important role. It is about how the user interacts with the product and what feelings come up. The product can be a technical device, a website, an app or even a company or service. The design determines how the users feel before, during and after the interaction.
The methods and techniques from UX design can be applied to ALL products, regardless of whether they are digital or not. The anticipated end users of the product are always the focus of the processes: At the beginning by defining requirements from the user's point of view (What is the product needed for? What goals does a user want to achieve with it, etc.). Then by aligning the content with the requirements. And then, again and again, by evaluating the content from the user's point of view.
Part of the processes in UX design are therefore user analyses based on various well-known methods from (market) research, especially behavioural psychology, which are carried out and from which certain measures are then concluded. So it's less about designing the user experience itself. Rather, it is about designing the framework conditions that, in the best case, lead to a positive impression and experience for the users.
What does UI Design mean?
UI stands for user interface and deals with the design of the user interface. UI design is primarily about the design of the user interface through visual and graphic design (colour schemes, typography, icons, layouts, images, etc.), the content and the appearance of the product, also in compliance with certain style guides and design patterns.
User interfaces consist of various components. Especially typical for digital products such as websites and apps are buttons, texts, input fields, animations, accordions and much more. Users come across all of these UI elements during use.
UI designers focus on the design of the product and thereby influence the visual impression of the product on the user.
Job profile UX Designer
UX designers are the interface between the users and the development team. Their task is to put themselves in the users' position during the software development process and to understand them. The user experience is at the centre of the work of UX designers. Therefore, they analyse the requirements, behaviours, emotions and attitudes of the users and define the right channels and points of interest. The aim of UX designers is to adapt the characteristics of the product to the corresponding target group in an ideal way.
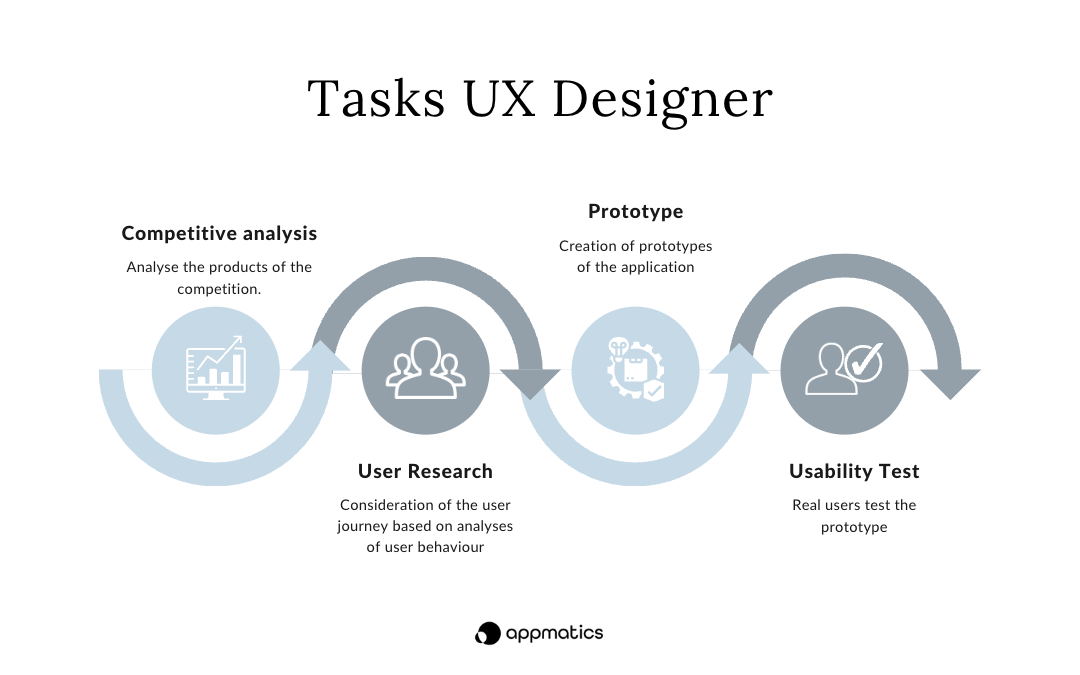
Following activities belong to the typical daily work of a UX designer:
-
Competitive analysis
By looking at successful products from the competition, you can make initial predictions about what the product should also have or what it should do better. Specific criteria for the own product are then defined.
-
User Research
As already mentioned, the users are the focus of the entire design process. At the beginning of a development phase, user research methods are used to identify requirements, behaviours and goals. Every single step of the user journey is looked at. The user journey is then summarised in flowcharts, flows or storyboards. The first requirements and drafts are then outlined from these..
-
Prototyping
Mock-ups can give a first look at the product with only a small effort. Together with these mock-ups and worked out prototypes, the idea of implementation is tested in advance. In this way, the ideal solution is identified step by step. Prototypes are usually created on paper or with the help of a modelling tool at the beginning. The prototypes are then further worked out and tested with real users within the framework of usability testing.
-
Usability Testing
In this step, real users test the current state of the product. It is important that the feedback from the user's interaction with the application is noted. Afterwards, the tests are evaluated. The results are used to iteratively revise the software in order to design it in the best possible way for the users.
The process cannot always be followed in reality - a UX designer is therefore always responsible for achieving a compromise between the interests of the users and the goals of the product together with the development team and other stakeholders. This often involves pragmatically selecting from the methods and using them at the right time in the interactive process.
Job profile UI Designer
UI design is not possible without UX design. As a UI Designer, you are particularly responsible for the design of the user interface. To do this, however, you must first know how it should be structured in order to provide the user with an optimal user experience.
UI Designer work closely with the UX team from the first sketch to the final prototype. They deal with colours, fonts, images, layouts and responsive design. They ensure a consistent look and feel and contribute their knowledge of style guides and design patterns. As a rule, they are the ones who translate the findings from the UX design into the graphic design and incorporate them iteratively.
UI is part of the UX!
Often the two job titles of UX/UI designer are also mixed. Even if the tasks and approaches of the professional fields are different, the fields have some overlaps. The greatest overlap is probably in the design of the user interface, even if the focus here is on different factors in each case. However, in the end, both parties pursue the same goal! Namely, to create an interface or a product that is intuitive and offers easy access to all functions of the product.
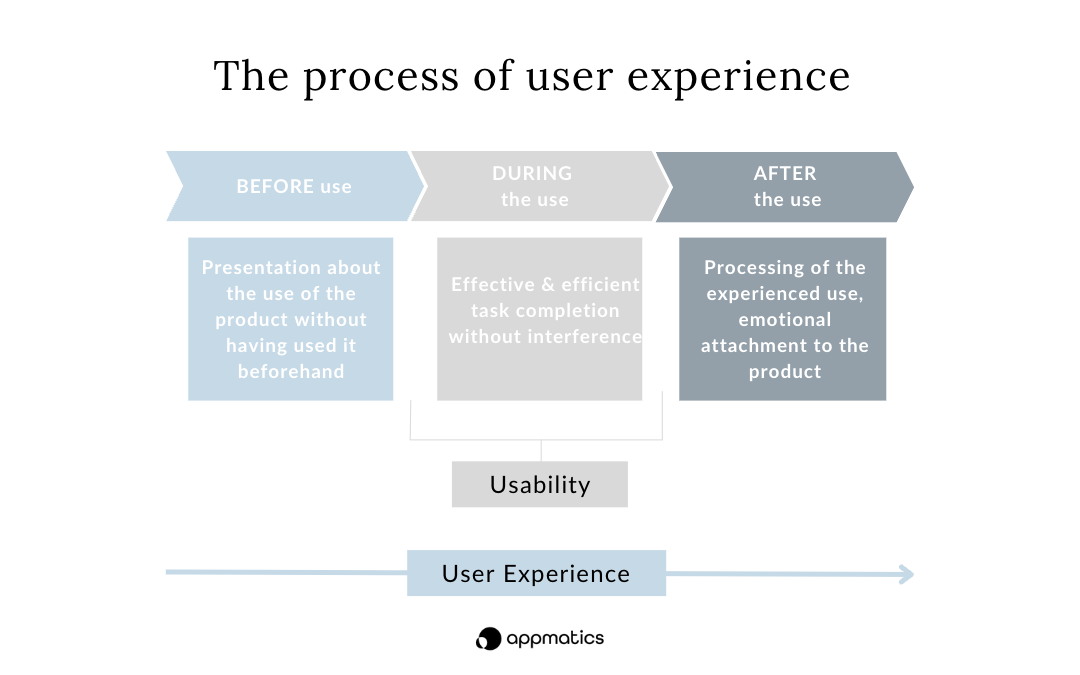
If you look at the concept of user experience, this also becomes clear: because the user experience is characterised by the entire usage process. User behaviour (usability) is only one part of it. The user experience (UX) begins BEFORE the product is used. At this point, it is initially only about the idea of what the product should do, without having used it beforehand. Usability then comes into play during use, because this is about the users' satisfaction during use. Do they succeed in solving tasks efficiently and effectively without any adverse effects of any kind? After use, it is particularly important how the users process the experience, whether they can identify with the product and have built up an emotional bond.
As you can see, a working interface is based on many factors and is very complex. Therefore, a comprehensive planning of the UX is the basis for a fully functioning UI in order to achieve a consistent overall concept and a positive experience of the product by the users.
UX Testing and UI Analysis at Appmatics
At Appmatics, we offer UX testing as test method for checking and evaluating.

-
Usability & UX Testing
Within the framework of usability testing, our UX team interviews and observes representative "average users" during the use of their product. As our customers, they receive meaningful results after a short time and can participate in the observation and analysis according to their own needs and capacities. Afterwards, we can prepare a detailed report for you, including video insights into the reactions of the test persons, and give you specific recommendations for further action.
-
UI analysis
At Appmatics, we carry out a UI analysis according to the Human Interface Guidelines and Material Design on request. These provide important guidelines for the design of iOS and Android apps.
Based on this, we analyse our clients' apps with a view to:App Architecture
app design
User interaction
System interaction
During the analysis, both user interface (UI) and partial aspects of user experience (UX) are considered and well-founded suggestions for optimisation are developed. Here too, the results are summarised in a detailed report. The report is interactive and can be used like a tablet app. Clickable navigation takes you immediately to the slides and results that you want to look at in more detail. In addition, the results and recommendations for action are presented again in a joint review meeting.
Our UX team will be happy to advise you in detail about the possibilities in the area of UX design and UI analysis.
